With cash wheat prices falling, farmers in many regions of the South are once again facing difficult decisions in their efforts to maximize returns on their crops. As prices dip below the breakeven threshold, alternative uses for wheat, such as grazing or baling, may offer improved profitability.
What follows is an example of a Wheat and Small Grains Decision Aid tool designed to help farmers analyze whether it is more beneficial to use wheat for grain, grazing, or hay. Evaluating the available alternatives is always prudent based on the relative prices of grazing, wheat hay, and grain, as well as the expected yields, production costs, and the availability and cost of harvesting or baling equipment. For this analysis, we assume that harvesting and baling equipment is custom-hired. However, from a cash cost perspective, owning your harvesting or baling equipment will influence the comparison of these two alternatives.
In contrast to last year, the hay alternative demonstrates higher profitability under similar production conditions in the Rolling Plains region of Texas. To estimate potential hay production, we assume grain yield corresponds to 40% of total biomass production. Thus, a wheat yield of 45 bushels per acre would produce a total biomass of approximately 3.1 tons per acre. Further, we assume that harvest and baling will yield 76% of this total biomass or about 2.3 tons per acre[1]. Estimating both grain and hay yield potential is essential when comparing these options.
The grazing option also appears more favorable, provided there is sufficient water, forage production, and livestock to maximize beef production.
Another way to approach this information is to determine at what price we must sell our hay (or grazing) to achieve a profit margin similar to that of wheat grain. The Decision Aid tool will use your data and costs to calculate hay and grazing breakeven prices (Graphs 1 and 2).
[1] (according to “Wheat Hay vs. Grain: A Comparison of Economic Opportunity” by Reagan Noland, Bill Thompson, and Clark Neely).
Graph 1. Break-Even Hay Prices
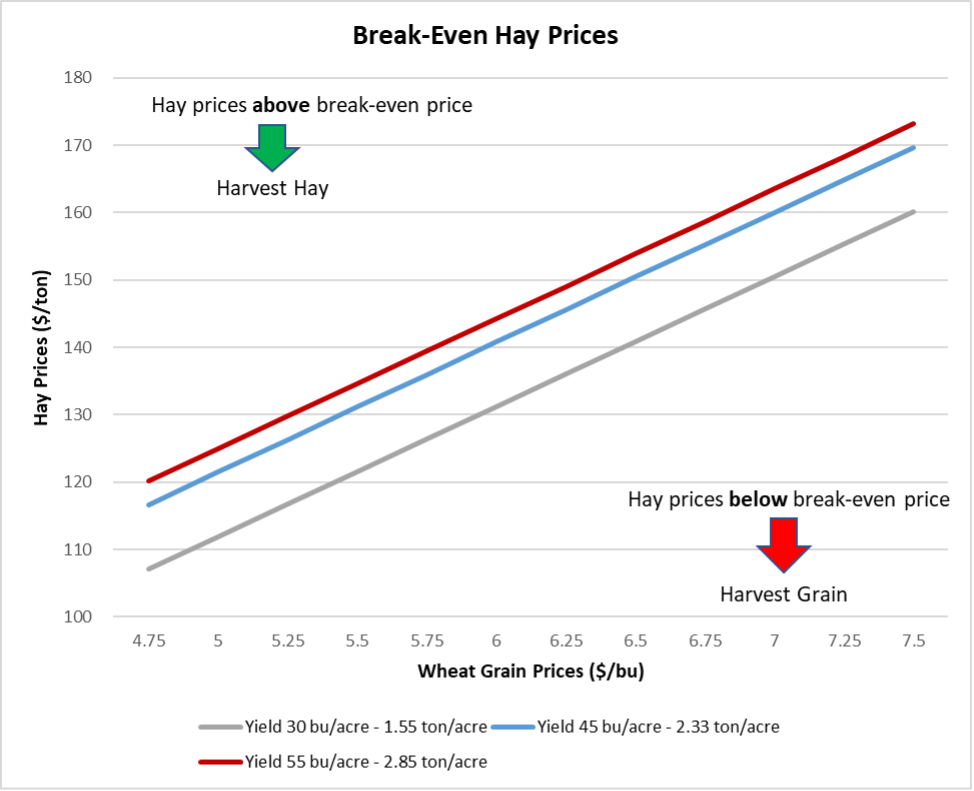
You might consider baling wheat if you can sell the hay above the breakeven price for hay given an expected grain price and yield. For example, with an estimated yield of 45 bushels per acre and a price of $5 per bushel, baling wheat would be more profitable if the net price per ton of hay exceeds $121 (assuming production of 76% of the total estimated biomass 2.3 tons per acre can be achieved).
Graph 2. Break-Even Grazing Prices
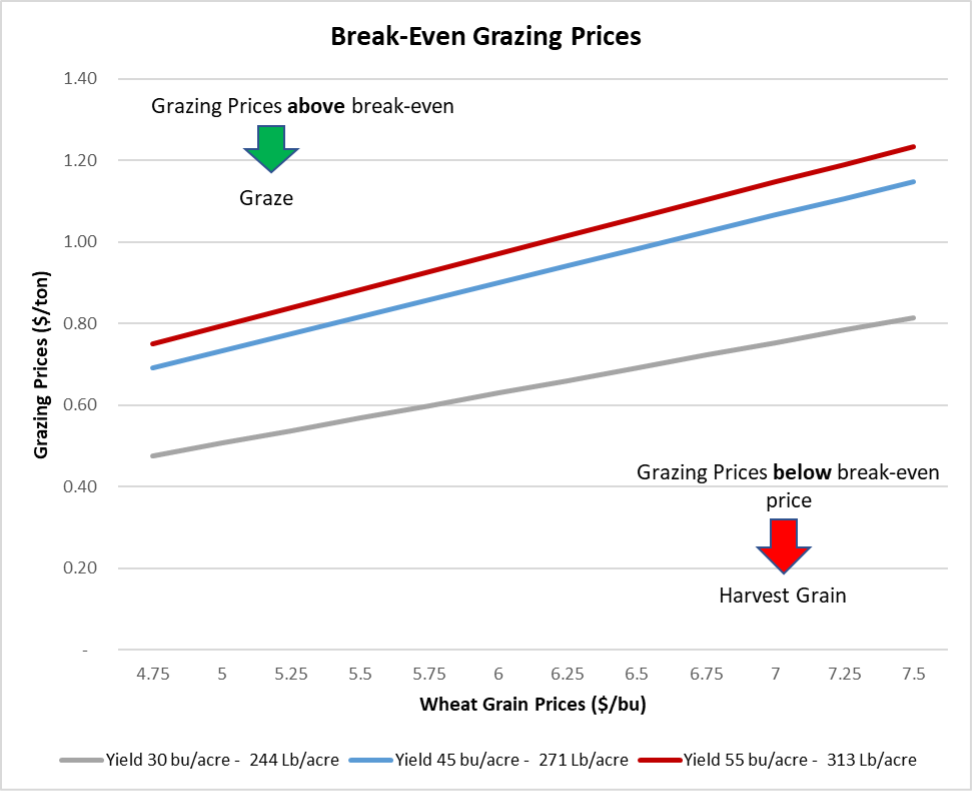
Similarly, for an estimated yield of 45 bushels per acre and a price of $5 per bushel, you would consider grazing out wheat if the grazing price exceeds $0.73 per pound of gain.
With weak wheat prices, exploring alternatives like grazing or hay may lead to improved financial outcomes in many areas of the South. The Wheat and Small Grain Decision Aids (Link) serves as an economic and financial tool to assist every farmer in making informed decisions. Using your own data, yields, prices, and costs is essential for effectively analyzing these alternatives. These examples reflect the current wheat conditions and expectations in the Texas Rolling Plains. Please let us know if you need assistance in using this decision aid to help you make better choices for your farm.
Abello, Pancho. “Wheat Alternatives: Maximizing Profitability in a Tough Market.” Southern Ag Today 5(9.1). February 24, 2025. Permalink

