On July 1, 2026, the “Poultry Grower Payment Systems and Capital Improvement Systems” ruling is set to go into effect. The ruling was set forth by the USDA Agricultural Marketing Service to amend the Packers and Stockyards Act of 1921. The most impactful change predicted is how it specifically addresses the way contract broiler growers are paid. The ruling requires live poultry dealers (integrators) to change the typical grower ranking systems, typically called “tournament pay”, to a system that establishes a minimum pay regardless of grower cost performance and allows for only positive pay incentives to be employed by integrators. For most integrators to meet this new requirement, it is expected that a standard minimum pay per pound of live broiler delivered to the processing plant will be established for all their growers. If you ask broiler growers, most will say they perceive this as a positive change, potentially making it easier to manage their businesses, and many will likely receive an increase in overall revenue. But this begs the question: will it positively affect all growers all the time, and is this the best way to help growers? And further, what affects revenue more – pay per pound or pounds out the door? In this and two upcoming contributions to Southern Ag Today, we look at what is driving the broiler revenue bus, to what extent does it have control, and finally, just how much a small change can mean to a grower’s bottom line.
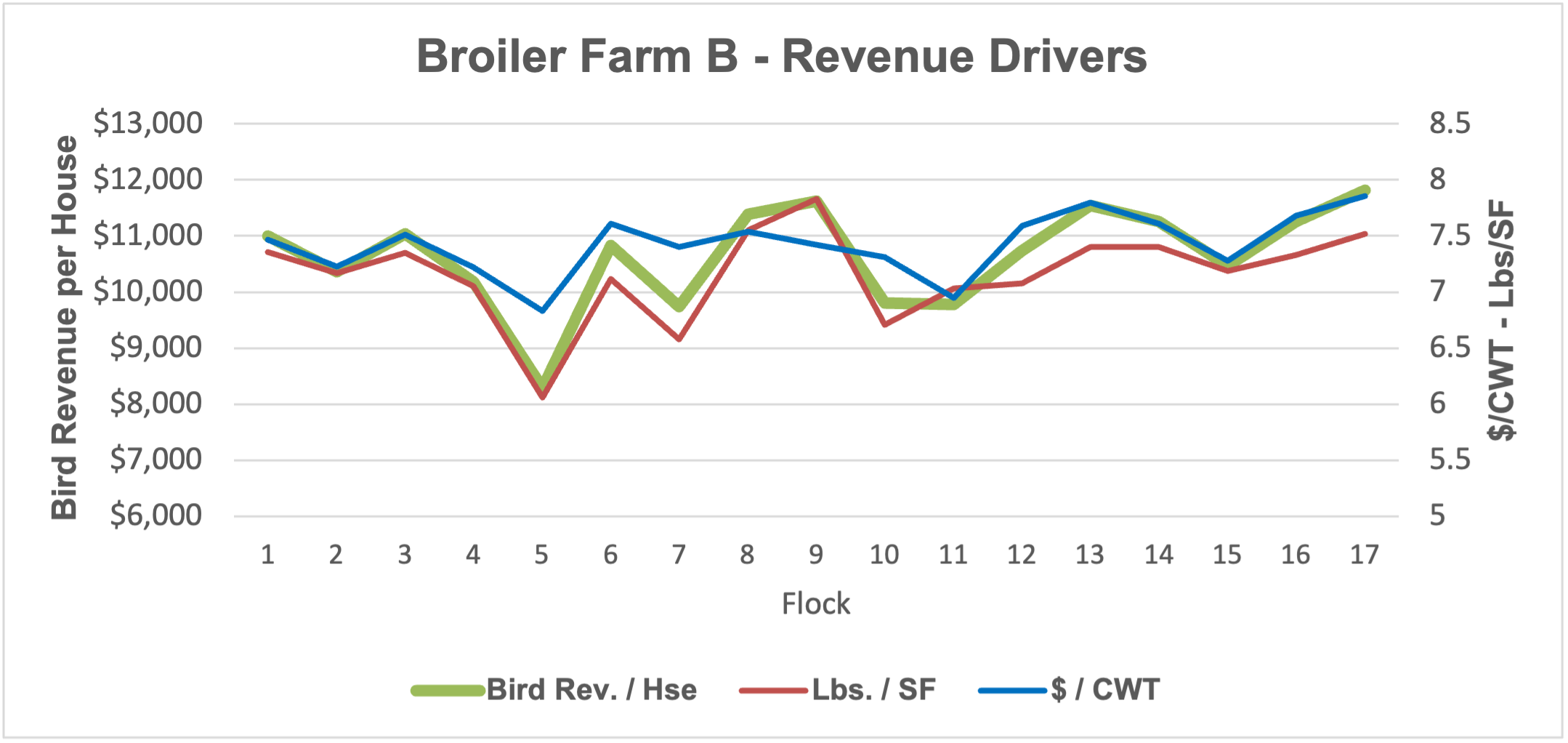
While an integrator may establish a fixed base, or minimum pay rate, that pay rate is only applied to pounds leaving the houses. There are many factors beyond the grower’s control that impact total pounds, such as bird placement rate (density), out-time between flocks, flock length, and mortality, especially when mortality is associated with a major disease event. While bird weight can be tied to farm management, the integrator makes the final decision on when to catch the birds, and a change of a couple of days can have a significant impact on pounds delivered. Out-time between flocks can also have significant impacts on pounds. Many things that affect out time are out of the control of both grower and integrator, like chick availability. To evaluate the question, I examined three and a half years of data from two broiler farms of the same size, age, technology, and in similar locations growing for the same integrator under the same tournament pay contract. The farms have different on-farm management, and Farm B is the better performer of the two. I compared bird revenue per house from 17 flocks to pounds per flock per square foot of housing (Lbs./SF) and pay per pound ($/CWT), nominally (Fig. 1a-b). A quick look at the graphs and it seems the green revenue line seems to mostly mirror the red Lbs./SF line. A closer look reveals that, while many flocks saw a directional movement of all three factors together, there were several flocks where $/CWT increased yet revenue decreased, driven by a decrease in Lbs./SF. There were also a few flocks where the opposite occurred and $/CWT decreased, yet revenue increased, driven by increased Lbs./SF. In these instances, Lbs./SF drives the revenue up or down despite opposite changes in pay rate. This would suggest that a simple pay rate fixation would not always equate to an increase in revenue, and that a decrease in pounds (often out of a grower’s control as indicated above) could easily overtake the potential positives of a marginal pay rate increase.
Figure 1a.
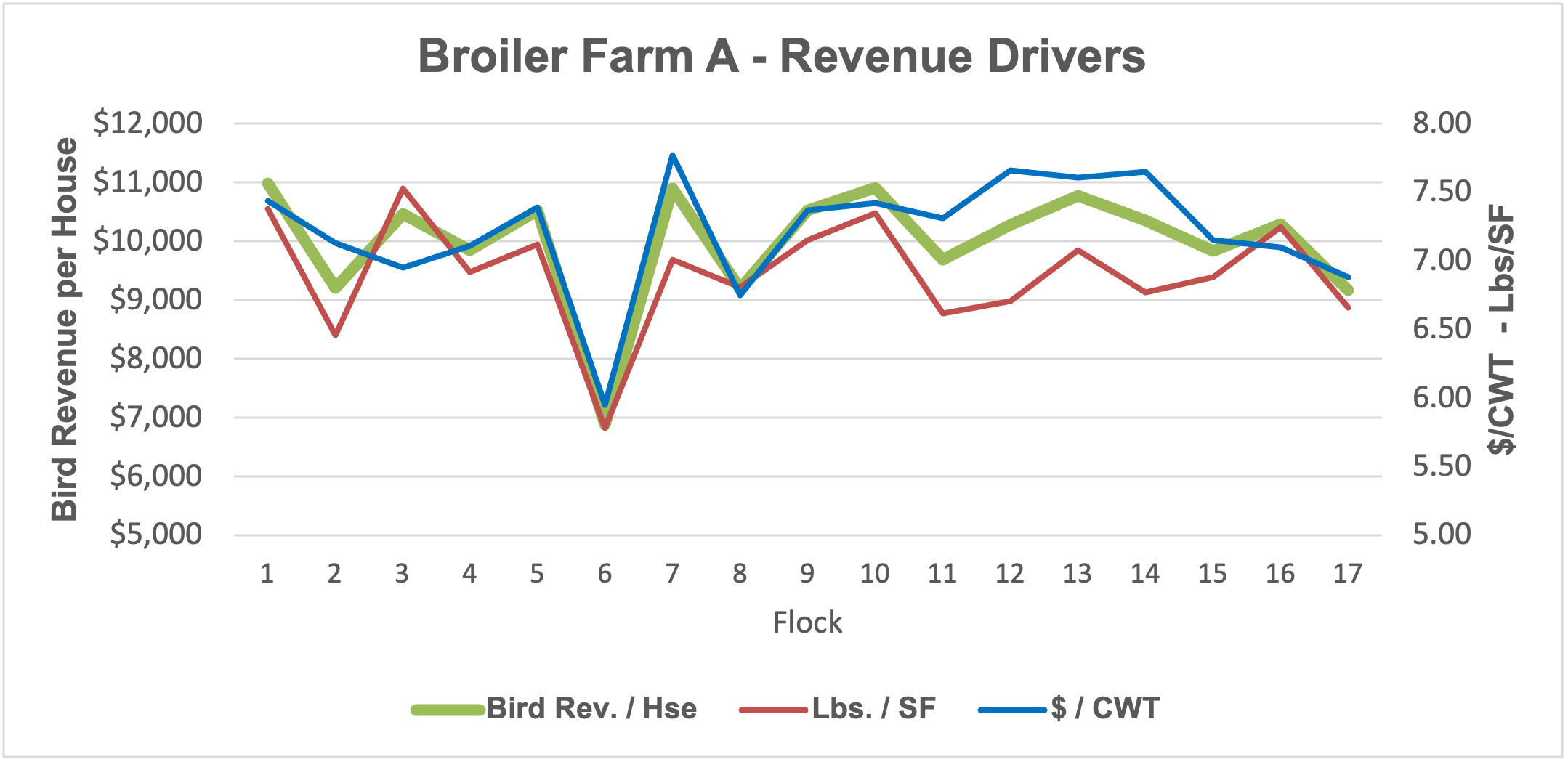
Figure 1b.
Brothers, Dennis. “Who’s Driving the Broiler Revenue Bus? (Part 1of 3).” Southern Ag Today 5(29.1). July 14, 2025. Permalink

