Consumers are interested in native plants (i.e., those present prior to European settlement) with heightened demand in recent years. Interestingly, positive perceptions of native plants are widespread but spending in the U.S. is uneven, with heightened spending among a relatively small group of consumers. Using a 2022 national survey of 2,066 U.S. households that purchase plants, consumer spending patterns reveal a clear segmentation story relative to native plant purchasing behavior. Consumers can be divided into three segments based on their perceptions of native plants: Native averse (32% of the sample), native curious (36%), and native enthusiast (32%). Approximately 20% of the sample (n=422) were from the USDA South region (i.e., Delaware, Washington D.C., Florida, Georgia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, West Virginia, Alabama, Kentucky, Missouri, Tennessee, Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, Texas; USDA, 2021). Of the Southern participants, 25% were native averse, 42% were native curious, and 32% were native enthusiasts.
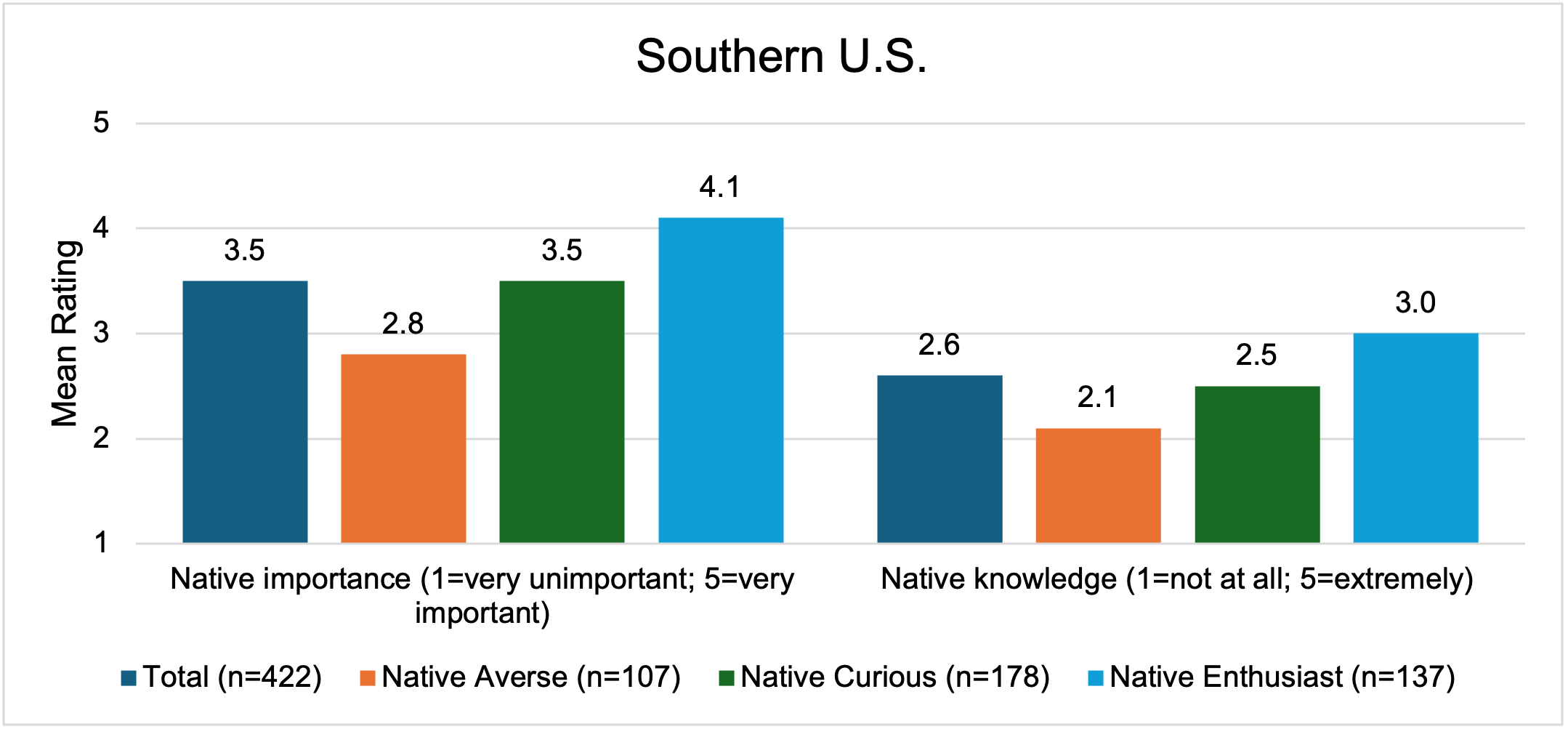
Several factors influenced segment membership including native plant perceptions, education, and plant purchasing behavior. Native enthusiasts and native curious consumers perceived native plants as providing many benefits (i.e., less maintenance, adapted to difficult sites, help water conservation, benefit the economy, improve biodiversity, are readily available, I know where to purchase native plants, are drought resistant, help pollinators, complements existing landscape, aid in natural habitat restoration, are aesthetically pleasing, and wildlife friendly) while native averse consumers did not share these perceptions. Rather, the native averse segment perceived native plants as not providing significant benefits over introduced species. The native enthusiasts also placed greater importance on native plants (in general) and reported higher subjective knowledge (Fig. 1). Similar results were observed in the U.S. and Southern region. In the South, 100% of native enthusiast members purchased native plants in 2021 (similar to 100% in the U.S. total sample), vs. 45% of native curious (46% in the U.S. total sample), and 34% of native averse segments (28% in the U.S. total sample). Education impacted segment membership, with native enthusiasts and native curious having higher education levels than the native averse group. Income did not influence segment membership, indicating that disposable income was not the driving factor behind these groupings, rather perceptions influenced subsequent plant spending behavior.
Figure 1. U.S. Consumers Perceived Importance and Knowledge of Native Plants
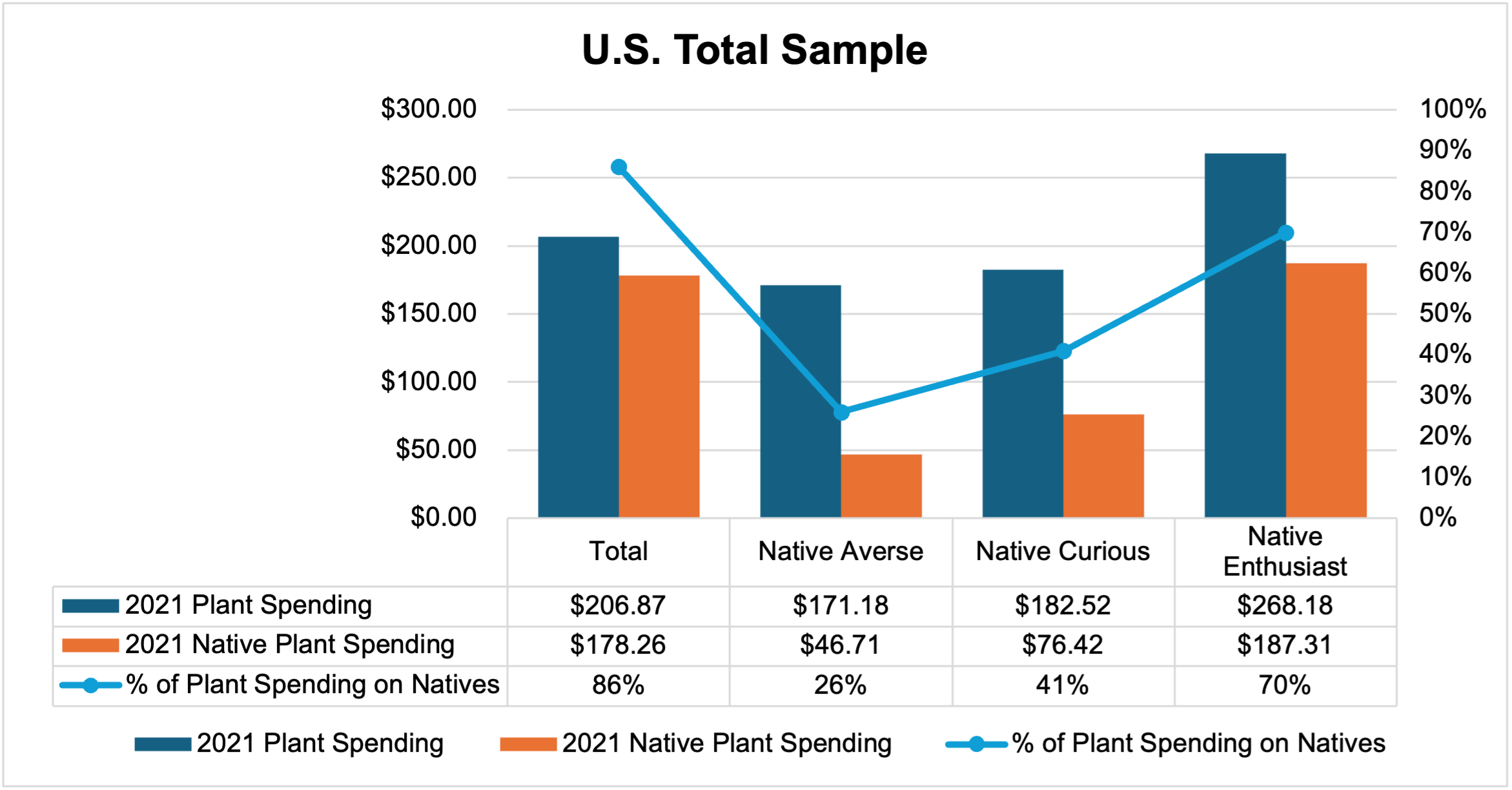
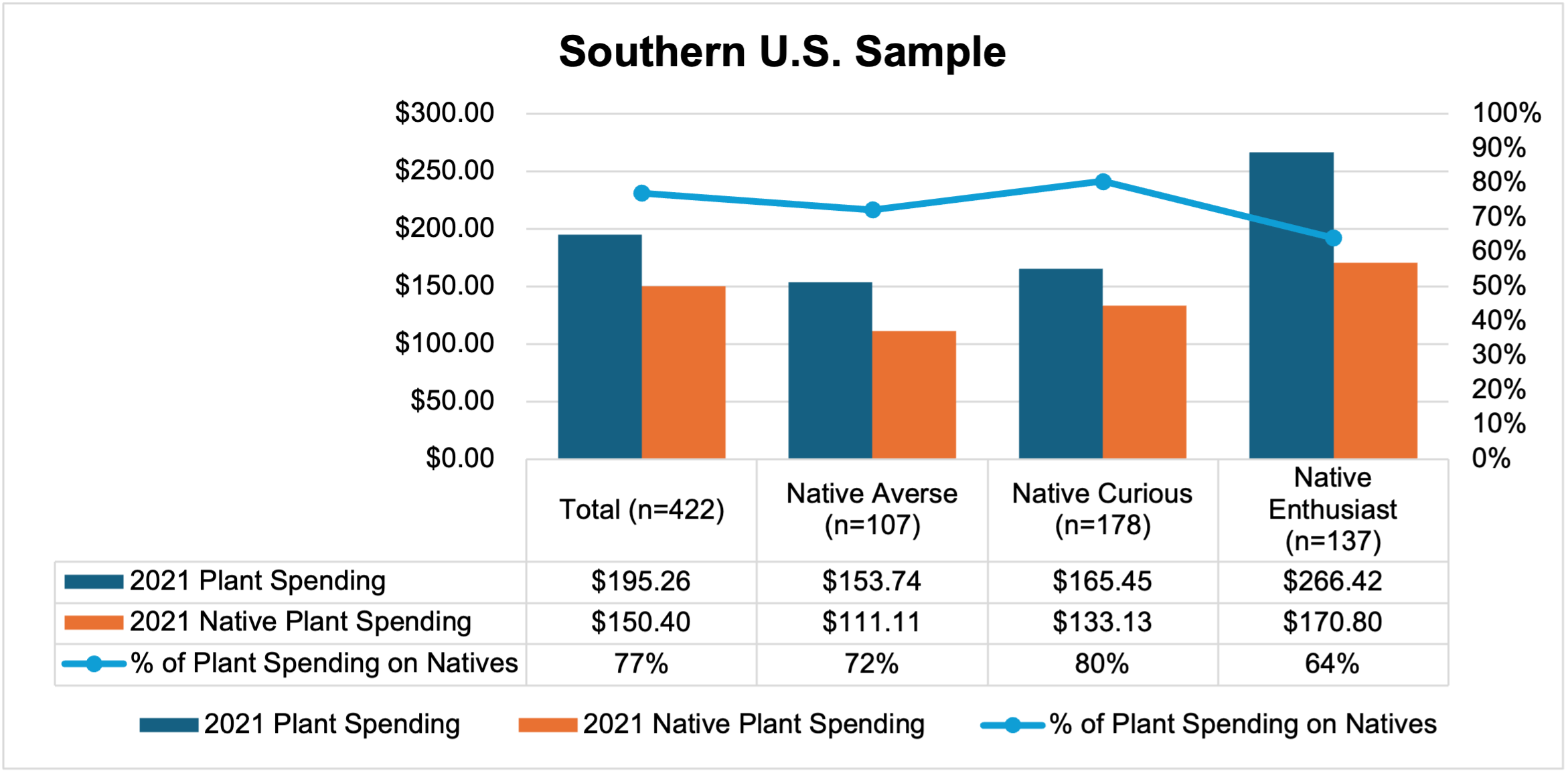
While all three segments purchase native and introduced plants, native plant expenditures are primarily driven by native enthusiasts and native curious members (Fig. 2). On average, in 2021, native enthusiasts spent $187 on native plants (70% of total plant spending), while native curious consumers spent $76 (41% of total plant spending) on native plants, and native averse spent $47 (26% of total plant spending) on native plants. In 2021 in the Southern region, native enthusiasts spent $171 on native plants (64% of total plant spending), while native curious consumers spent $133 on native plants (80% of total plant spending), and native averse spent $111 on native plants (72% of total plant spending). Of note, total plant spending was higher among native enthusiasts in both the total and Southern samples relative to the native curious and native averse which were not significantly different. This implies that the native enthusiast segment is spending more on plants in general and are likely seeking out native plants when they are available.
Figure 2. U.S. Consumer Native and Introduced Plant Spending Behavior In 2021 (n=2066).
These patterns point to potential growth in native plant sales through increasing per-customer spending among consumers who already buy plants and view native plants favorably. A small shift in the native curious consumers’ plant budgets to purchase more native plants could generate a sizable gain in total native plant sales because of the size of the segment and their receptiveness to native plants. For growers, retailers and landscapers, strategies that increase confidence in native plant selection is key. For example, clear labeling, aesthetic assortments and bundling native plants with information may be more effective than broad awareness campaigns. These strategies may be more impactful given that there is evidence that native plants are not always clearly identified at retail (Brzuszek and Harkess, 2009) and that native plants may be perceived as less desirable than introduced plants (Gillis and Swim, 2020). Thus, providing clear point-of-sale information about the plants and their benefits while demonstrating their aesthetic appeal may aid in convincing members of the native curious segment to purchase more native plants.
References:
Brzuszek RF, Harkess RL. 2009. Green industry survey of native plant marketing in the southeastern United States. HortTechnology 19:168-172. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTTECH.19.1.168
Gillis AJ, Swim JK. 2020. Adding native plants to home landscapes: The roles of attitudes, social norms, and situational strengths. J Environ Psych. 72: 101519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2020.101519
US Department of Agriculture. 2021. Regions – states by census region and division. https://www.ars.usda.gov/northeastarea/beltsville-md-bhnrc/beltsville-humannutrition-research-center/docs/regions/. [accessed 26 Feb 2024].
Acknowledgements: This research was supported by a grant from the Horticultural Research Institute (‘‘HRI’’). Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of HRI.
Source: Rihn, A.L., A. Torres, B. Behe, and S. Barton. 2024. Unwrapping the native plant black box: Consumer perceptions and segments for target marketing strategies. HortTechnology. 34(3): 361-371. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTTECH05401-24.
Rihn, Alicia, and Pralhad Bajgain. “U.S. Native Plant Spending and Customer Segments: A Southern Perspective.” Southern Ag Today 6(6.5). February 6, 2026. Permalink

